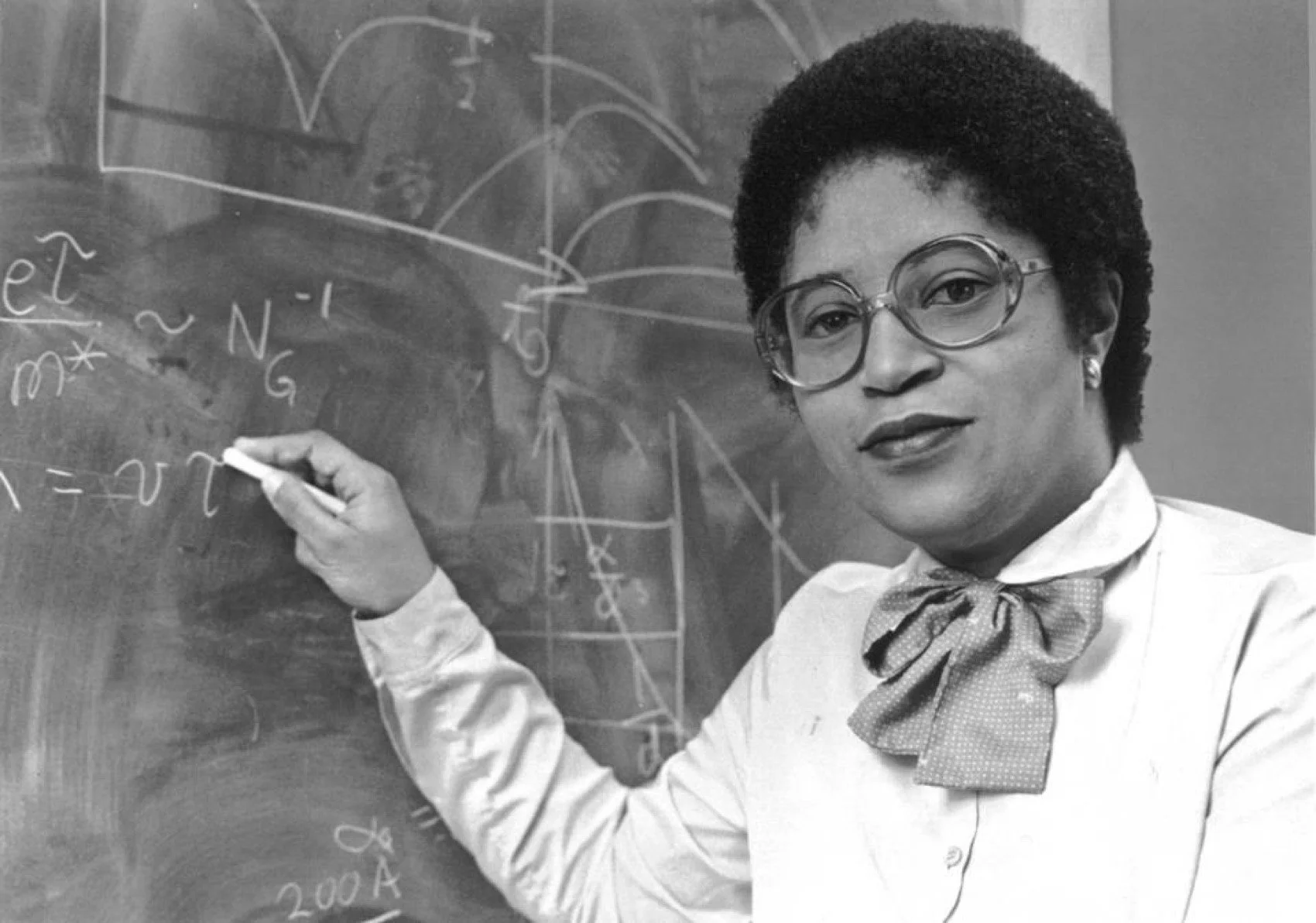Cloud Storage Explained: Where Your Files Really Live
"It's saved to the cloud" has become a common phrase, but what does it actually mean? Understanding cloud storage helps you make better decisions about backing up and accessing your important files.
What "The Cloud" Actually Is
Despite its ethereal name, the cloud is quite tangible—it's a network of physical servers housed in secure data centers around the world. When you save something "to the cloud," you're storing it on these remote servers rather than on your device.
This remote storage offers several advantages:
Your files remain accessible even if your device is lost or damaged
You can access your information from multiple devices
Storage capacity can expand without upgrading your physical device
Service providers implement security and backup measures
How Cloud Storage Works With Apple Devices
Apple's iCloud seamlessly integrates cloud storage into your daily experience:
Photos taken on your iPhone appear on your iPad and Mac
Documents created on your Mac are accessible from your iPhone
App data synchronizes across devices
Backups happen automatically in the background
This integration happens through your Apple ID, which serves as your identity across Apple's ecosystem.
Common Cloud Storage Questions
Understanding these basics helps solve common confusion:
Storage limitations: Free accounts typically include 5GB, with options to purchase more
Internet requirements: You need an internet connection to upload/download files
Privacy considerations: Providers like Apple encrypt your data for security
Local vs. cloud: Some files exist only in the cloud, while others maintain local copies
Optimizing Your Cloud Experience
Make the most of cloud storage with these approaches:
Be selective about what syncs to the cloud if you have limited storage
Use iCloud Photos options like "Optimize Storage" to save device space
Regularly review what's being backed up to avoid unnecessary storage use
Consider which services (Apple, Google, Microsoft) best meet your needs
Key Vocabulary
Cloud Storage: Remote servers that store your files and data
Sync: The process of updating files across multiple devices
iCloud Drive: Apple's cloud storage service for documents and files
Data Center: Physical facility housing multiple servers for cloud services
Encryption: Security measure that protects your data from unauthorized access
Historical Spotlight: Dr. Shirley Ann Jackson
Dr. Shirley Ann Jackson's groundbreaking research in theoretical physics laid crucial groundwork for technologies that would eventually enable cloud computing. As the first African-American woman to earn a doctorate from MIT (1973), Dr. Jackson conducted pioneering work in telecommunications research at Bell Laboratories, where her studies in electronic properties of materials contributed to the development of technologies essential for today's internet infrastructure. Her work on subatomic particles helped advance our understanding of semiconductor materials crucial to modern computing. Beyond her research, Dr. Jackson's distinguished career includes serving as chairman of the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission and president of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. Her contributions to foundational science directly enabled the massive data transmission capabilities that cloud storage systems require to function seamlessly across global networks.